
Nat Rev Neurosci 14:365Ĭheavegatti-Gianotto A, de Abreu HMC, Arruda P, Bespalhok Filho JC, Burnquist WL et al (2011) Sugarcane (Saccharum X officinarum): A Reference Study for the Regulation of Genetically Modified Cultivars in Brazil.
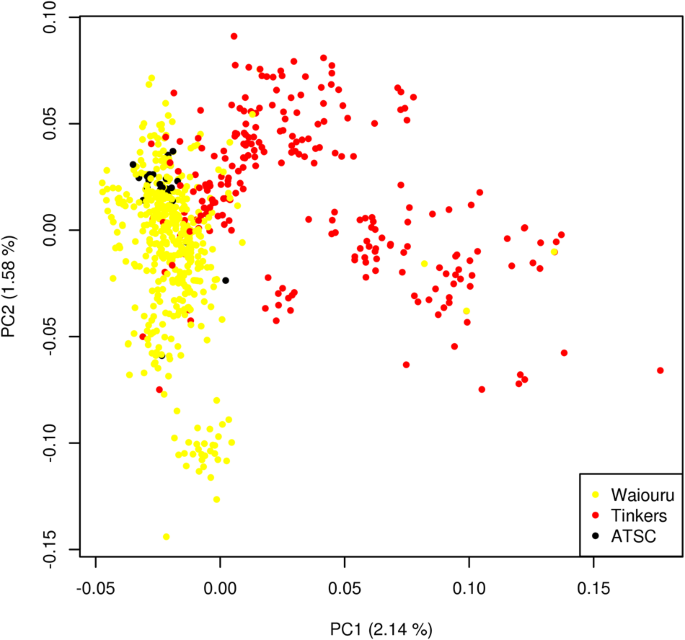
160īutton KS, Ioannidis JPA, Mokrysz C, Nosek BA, Flint J et al (2013) Power failure: why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Plant Biotechnol J 7:347–354īutler DG, Cullis BR, Gilmour AR, Gogel BJ (2009) ASReml-R reference manual. Bioinformatics 34:407–415īundock PC, Eliott FG, Ablett G, Benson AD, Casu RE et al (2009) Targeted single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery in a highly polyploid plant species using 454 sequencing. Crop Sci 47:1082–1090īlischak PD, Kubatko LS, Wolfe AD (2018) SNP genotyping and parameter estimation in polyploids using low-coverage sequencing data. Stemma Press, Woodsbury, MNīernardo R, Yu J (2007) Prospects for Genomewide Selection for Quantitative Traits in Maize. Genome 61:449–456īernardo R (2010) Breeding for Quantitative Traits in Plants. Crop Sci 60:656–665īastien M, Boudhrioua C, Fortin G, Belzile F (2018) Exploring the potential and limitations of genotyping-by-sequencing for SNP discovery and genotyping in tetraploid potato. Overall, we show that including allele dosage can improve genomic selection in highly polyploid species under higher frequency of different heterozygous genotypic classes and high dominance degree levels.Īmadeu RR, Ferrão LFV, de Oliveira IB, Benevenuto J, Endelman JB et al (2020) Impact of dominance effects on autotetraploid genomic prediction. When the frequency of heterozygous genotypes in the population was low, such as in the sugarcane and sweet potato datasets, there was little advantage in including allele dosage information in the models. Including dominance effects were highly advantageous when using diploidized markers, leading to mean predictive abilities which were up to 115% higher in comparison to only including additive effects. For the simulated datasets, including allele dosage information led up to 140% higher mean predictive abilities in comparison to using diploidized markers. We applied these models using estimates of ploidy and allele dosage to sugarcane and sweet potato datasets and validated our results by also applying the models in simulated data. We adapted the models to build covariance matrices of both additive and digenic dominance effects that are subsequently used in genomic selection models. In this study, we expanded the methodology used for genomic selection in autotetraploid to higher (and mixed) ploidy levels.
PREDICTIONS ASREML HOW TO
Several studies have shown how to leverage allele dosage information to improve the accuracy of genomic selection models in autotetraploid.
Including allele, dosage can improve genomic selection in highly polyploid species under higher frequency of different heterozygous genotypic classes and high dominance degree levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
